Oymantepe (East Sadak)
section-f4723ef
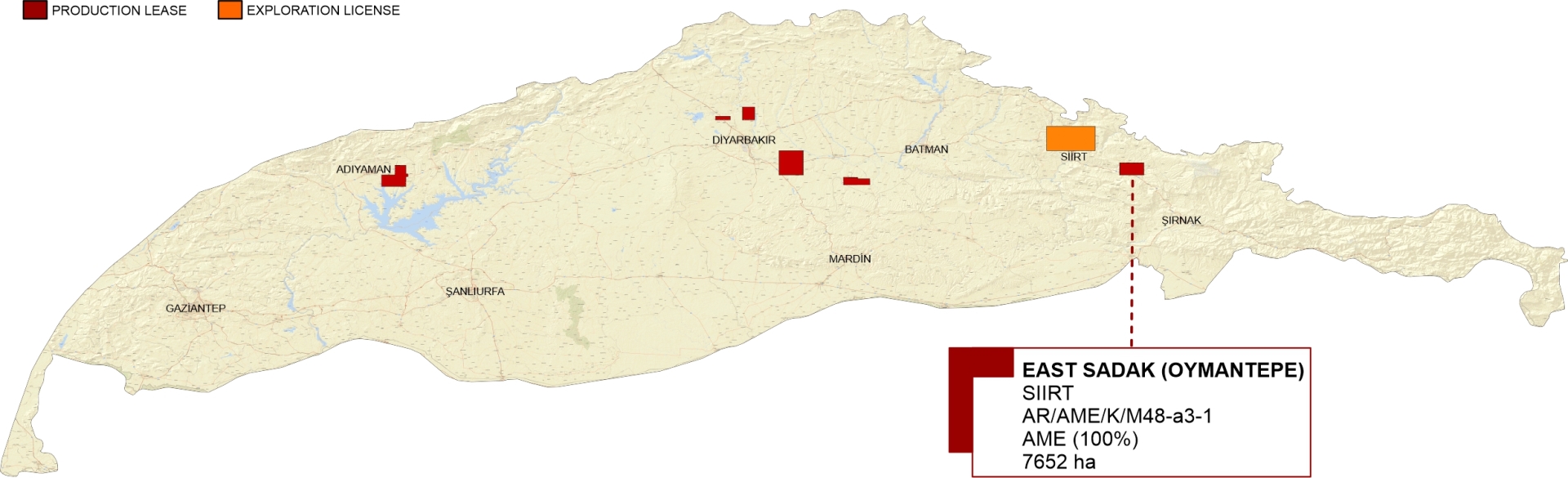
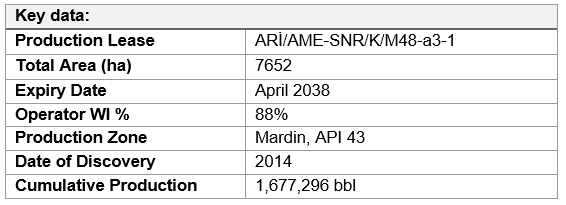
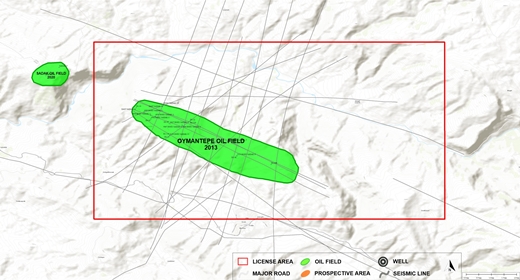
East Sadak lease covers an area of 7,652 hectares near the city of Siirt. It is on the same structural trend as the most productive oil fields in the SE Anatolian Basin.
There are two surface anticlines within the lease area. The one to the West (Oymantepe), East Sadak-1 well was drilled in 2014, and the lightest oil gravity was ever found in the country. Since then, the Oymantepe field has been developed by drilling 17 (of which 7 were sidetracked and one well was sidetracked twice) from 15 well pads. The other surface anticline to the SE corner has remained as an undrilled structure that shares the same structural and stratigraphic features with the Oymantepe field.
The main reservoir units are Upper Cretaceous Beloka Formation and Mardin Group carbonates, and Jurassic Cudi Group carbonates which is a deeper target, and none of the East Sadak wells penetrated this reservoir yet. On the other hand, a new deep amplitude play concept has been developed to test Cudi Group reservoirs by drilling a well of 3,800m TD.
Beloka Formation is composed of fractured limestones and dolomites; its low matrix porosity (4-6%) is enhanced by leaching and fracturing. Mardin Group carbonates have higher matrix porosity up to 15%. Starting with East Sadak-6 (2018), the open-hole design has been used to complete both reservoirs to prevent formation damage.
Even though the Garzan Formation is one of the main producing reservoirs in the region, it has not been a producing interval in the Oymantepe oil field. On the other hand, its behind-pipe potential has been studied to add it to the oil production pool.
During the drilling of the carbonate interval of the Paleocene age Upper Sinan formation, significant oil shows were observed even though heavier drilling mud was used during the drilling of this upper section. AME has also been studying to test the HC potential of this reservoir with a shallow well design as a part of its field development plans.
In the year 2022, ES9/ES9R and ES-15/15S wells were drilled. ES-15S (TD: 1,973m) could not cross a fault due to sloughing shales to enter the oil pool and therefore had to be abandoned. ES-9R (TD: 2,890m) tested oil, was put on production with an initial rate of 40 bopd.
In the year 2023, a total of three wells were drilled: ES-16, ES-5S, and ES-17. The ES-16 well was temporarily abandoned due to encountering drilling issues at the near-surface fault. The ES-5S infill deviated well was spudded in July 2023 and TD’d at a depth of 2645m within the Mardin Group carbonates. Even though high gas readings were recorded during the drilling of the Beloka Formation, this interval P&A’d and Garzan Formation was perforated. The ES-17 well was spudded in October 2023 and TD’d at a depth of 2573m in the Beloka Formation. The workover operations continue both in ES-05S and ES-17 wells as of March 2024.